LIQUID CRYSTAL CELL.
The invention concerns a liquid crystal cell in accordance with the generic term of the requirement 1.
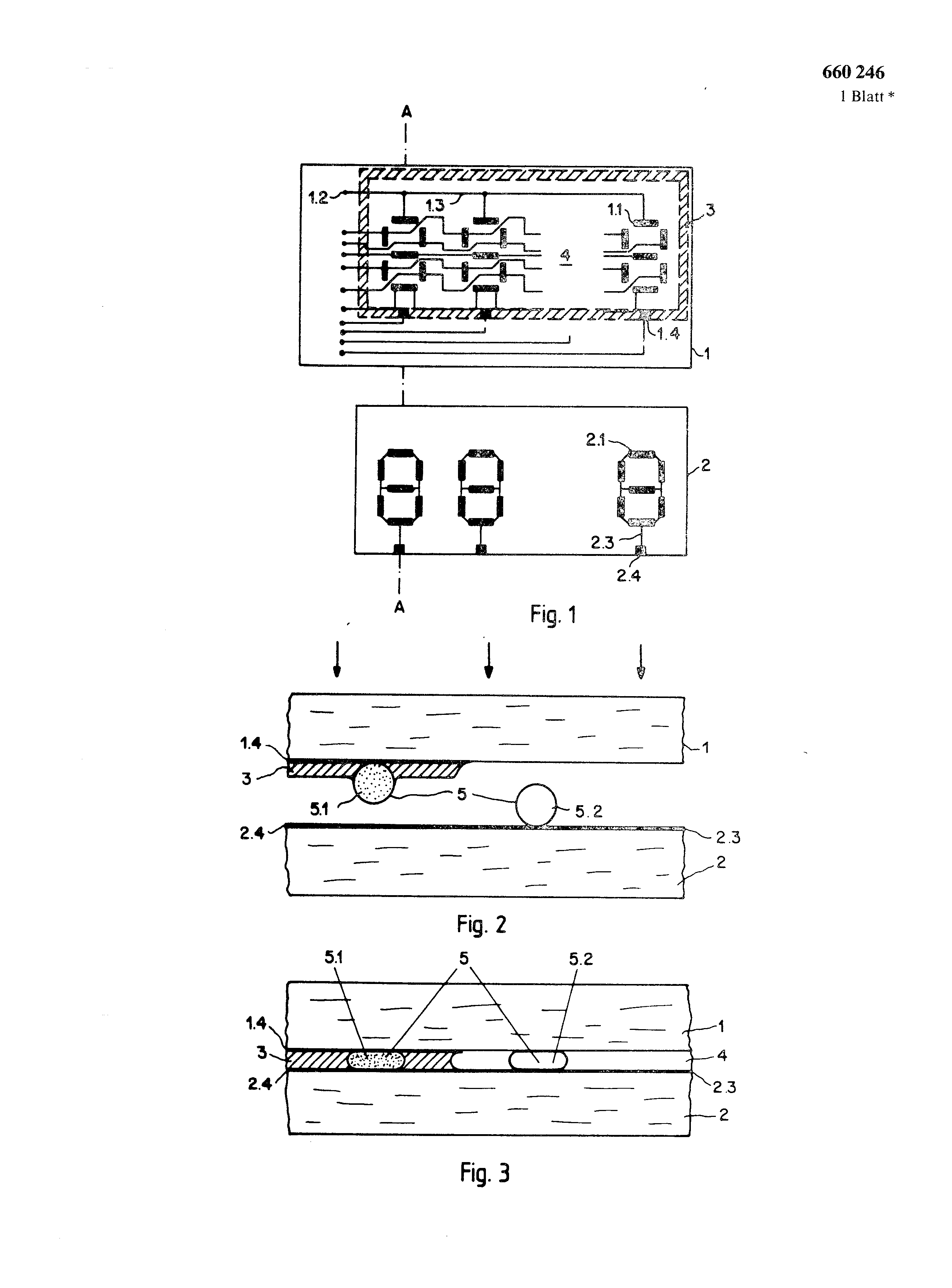
With a liquid crystal cell the thickness of the liquid crystal layer should be as constant as possible essentially determining distance of the two mother boards over the entire surface of the cell. To reach a constant distance leaves itself among other things by bringing in spacers between the Trägerplatten.
Admit are liquid crystal cells with glass balls (DE-AS 2,815,405), glass fibers (GB 2,050,637 A) or Kohlenstofffasem (CH 634,422) as Abstandshalter.
Spacers from electrically leading material serve to form apart from their function as distance elements, dog-legs between electrode layers of both mother boards S5. They usually are outside of the liquid crystal layer in the edge verteilt.
With the well-known spacers if providing liquid crystal cells extreme temperatures (- 30*, + 80*) and/or high air humidity (90%) are suspended, then frequently defect arises. At low temperatures negative pressure blisters, so-called Vakuolen, appear in the liquid crystal layer. These Vakuolen are caused by the different thermal coefficients of expansion of the liquid crystal layer and the remaining cell material, among other things the spacer. At high temperatures and high air humidity it comes to corrosion-conditioned defects. Those usually as sticking bar implemented edge pours up. In the edge distributed electrically leading spacer can thereby the contact to the electrode layers lose. Contact contacts are the result. If the liquid crystal cell in transmission with dark background is operated, then spacers from glass are visible within the liquid crystal layer as bright bright points and produce so a clarification of the background. This leads to a bad contrast. Particularly disturbing spacers from glass work in colored liquid crystal layers, since glass cannot be dyed of only few txm to thickness sufficiently intensively. If the number of spacers from glass in the liquid crystal layer is lowered, then break this under the Druckbelastung.<br necessary with the manufacturing of the liquid crystal cell/>
Task of the invention is it to indicate a liquid crystal cell of the kind initially specified which is functional at extreme temperatures and high air humidity roll and exhibits altogether a higher contrast. For the solution of this task a liquid crystal cell is suggested after the generic term of the requirement 1, which according to invention the characteristics of this requirement of characteristics mentioned aufweist.
The advantages reached by the invention are to be seen essentially in the fact that by the rubber elasticity of the spacers the distance of the two mother boards can be reduced at low temperatures so far that no Vakuolen arise. Leading, likewise elastic Abstanshalter in the edge, the electrically at high temperatures and high air humidity know, if they are flexibly deformation with the Solioder normal distance of the Trãgerplatten, when swelling the edge by decrease of their deformation in safe contact with the electrode layers bleiben.
Contact contacts are avoided thereby. Also the number of spacers in the liquid crystal layer can be reduced, since elastic spacers under the pressure load usual with the manufacturing do not break. This guarantees a increased contrast of the announcement. Beyond that elastic material can be dyed easily and be adapted to the colour of the liquid crystal layer. The spacers do not step then in the liquid crystal layer practically no more disturbing into Erscheinung.
Further advantages, characteristics as well as preferred arrangements of the invention, like it also in the dependent A liquid crystal display cell including a liquid crystal layer contained between two plane-parallel support plates provided with electrode layers on their mutually inward facing surfaces as well as a border. The support plates are held apart within a predetermined separation range by means of spacers. Those spacers distributed in the border are electrically conductive and serve as contact bridges between through-contact points on the support plates. Rubber-like elastic particles, e.g. from a silicone elastomer, are used as spacers to prevent low pressure bubbles in the liquid crystal layer at temperatures of -30 DEG C. as well as to prevent loss of contact between the through-contact points. The rubber-like elastic particles, between the through-contact points are electrically conductive. 1. A liquid display cell comprising: two lane-parallel support plates having mutually inward facing surfaces provided with respective electrode layers and a border surrounding said electrode layers; a liquid crystal layer switchable between two optically distinguishable states contained in a space between said plates and said border; and rubber-like elastic particles disposed between said plates and serving as spacers to maintain said plates separated within a predetermined separation range. 2. A liquid crystal cell as in claim 1, wherein the rubber-like elastic particles are elastically deformable as long as the support plates have a separation in a range of about .+-.50% of a predetermined nominal separation. 3. A liquid crystal cell as in claim 1, wherein the rubber-like elastic particles have a spherical shape. 4. A liquid cyrstal cell as in claim 2, wherein the rubber-like elastic particles have a spherical shape. 5. A liquid crystal display cell as in claim 4, comprising: said rubber-like elastic particles being disposed between the support plates at definite points, in said border, and inside the liquid crystal layer but not between electrode layers which lie across from each other. 6. A liquid crystal display cell according to claim 4, comprising: said plates having opposed through-connection contact points; and electrically conductive of said elastic particles disposed between said contact points to electrically connect said contact points. 7. A liquid crystal display cell according to claim 6, comprising: said through-connection contact points being located in said border. 8. A liquid crystal cell as in claim 1, wherein said rubber-like elastic particles comprise: electrically conductive rubber-like elastic particles distributed in the border and serving as spacers. 9. A liquid crystal cell as in claim 8, wherein the vast majority of the electrically conductive rubber-like elastic particles in the border have no mutual contact. 10. A liquid crystal cell comprising: two plane-parallel support plates having mutually inward facing surfaces provided with respective electrode layers and a border surrounding said electrode layers; a liquid crystal layer switchable between two optically distinguishable states contained in a space between said plates and said border; and rubber-like elastic particles disposed between said plates and serving as spacers to maintain said plates separated within a predetermined separation range; wherein said rubber-like elastic particles comprise: a base material formed of a silicone elastomer. 11. A liquid crystal display cell as in claim 10, wherein the electrically conducting rubber-like elastic particles comprise: a silicone elastomer filled with an electrically conductive pigment. 12. A liquid crystal display cell as in claim 11, wherein said electrically conductive pigment is selected from the group consisting of soot, graphite and metal powder. 13. A liquid crystal display cell as in claim 10, wherein said silicone elastomer has a color matched to the color in the surrounding liquid crystal cell for the rubber-like elastic particles distributed inside the liquid crystal layer.