STROKE DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY ASSISTANCE SYSTEM, STROKE STATE INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICE, AND STROKE STATE INFORMATION PROVIDING PROGRAM
The present invention relates to a system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke, specifically a system which can easily provide supportive information so that the type of stroke can be determined appropriately and corresponding treatment strategy can be implemented. A conventional watch over system is described using a device of medical image processor P100 shown in Thus, information for determining a necessary treatment to cerebral infarction is provided by visualizing the progress of cerebral infarction at each site of the brain, (see patent literature 1). 1. JP 2016-73542 The device of medical image processor P100 described above needs to be improved in some points as follows. The device of medical image processor P100 calculates the recoverability based on a local blood flow in a subject's brain tissue. Therefore, it is premised on application to recanalization therapy which removes thrombi formed in arteries of the brain and restores blood flow in brain tissue that is in ischemia. On the other hand, there are several types of strokes that do not accompanied with intracerebral hemorrhage, including non-cardiogenic lacunar infarction, non-cardiogenic atherothrombotic cerebral infarction, and cardiogenic cerebral embolism, and therapeutic strategies are different depending on the type of cerebral infarction. Thus, it is difficult for a physician or the like who does not have sufficient knowledge about stroke to determine properly the type of stroke and implement corresponding therapeutic strategy. Accordingly, it is an object of the present invention to provide a system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke which can easily provide supportive information so that the type of stroke can be determined appropriately and corresponding treatment strategy can be implemented. The object of the present invention is achieved by the following inventions. (1) A system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke which has a device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke and a device for providing information about state of stroke, uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed, to provide information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that assists diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and is characterized in that
(2) A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke which uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed to assist diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and has
(3) A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke characterized in that
(4) A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke characterized in that
(5) A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke characterized in that
(6) A program for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that makes a computer function in the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed, to assist diagnosis/treatment of stroke, as
(7) A model for determination of the type of cerebral infarction, characterized by making a computer function as a unit of stroke type determiner that uses the information about infarction regions wherein the size, number, and position of the infarction region, responsible vessels for the infarction region, and their number are determined and the information about occlusions/stenoses wherein the presence or absence of intracranial stenoses is determined, for a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring, by using the information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images, to determine the type of cerebral infarction, and that
(8) A model for determination of cerebral infarction regions, characterized by making a computer function as a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI and ADCmap of the brain and a unit of cerebral infarction region determiner that determines a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring by using the information of DWI and ADCmap, and that
(9) A model for determination of responsible vessels, characterized by making a computer function as a unit of responsible vessel determiner that determines responsible vessels from the information about three-dimensional position of a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring, and that
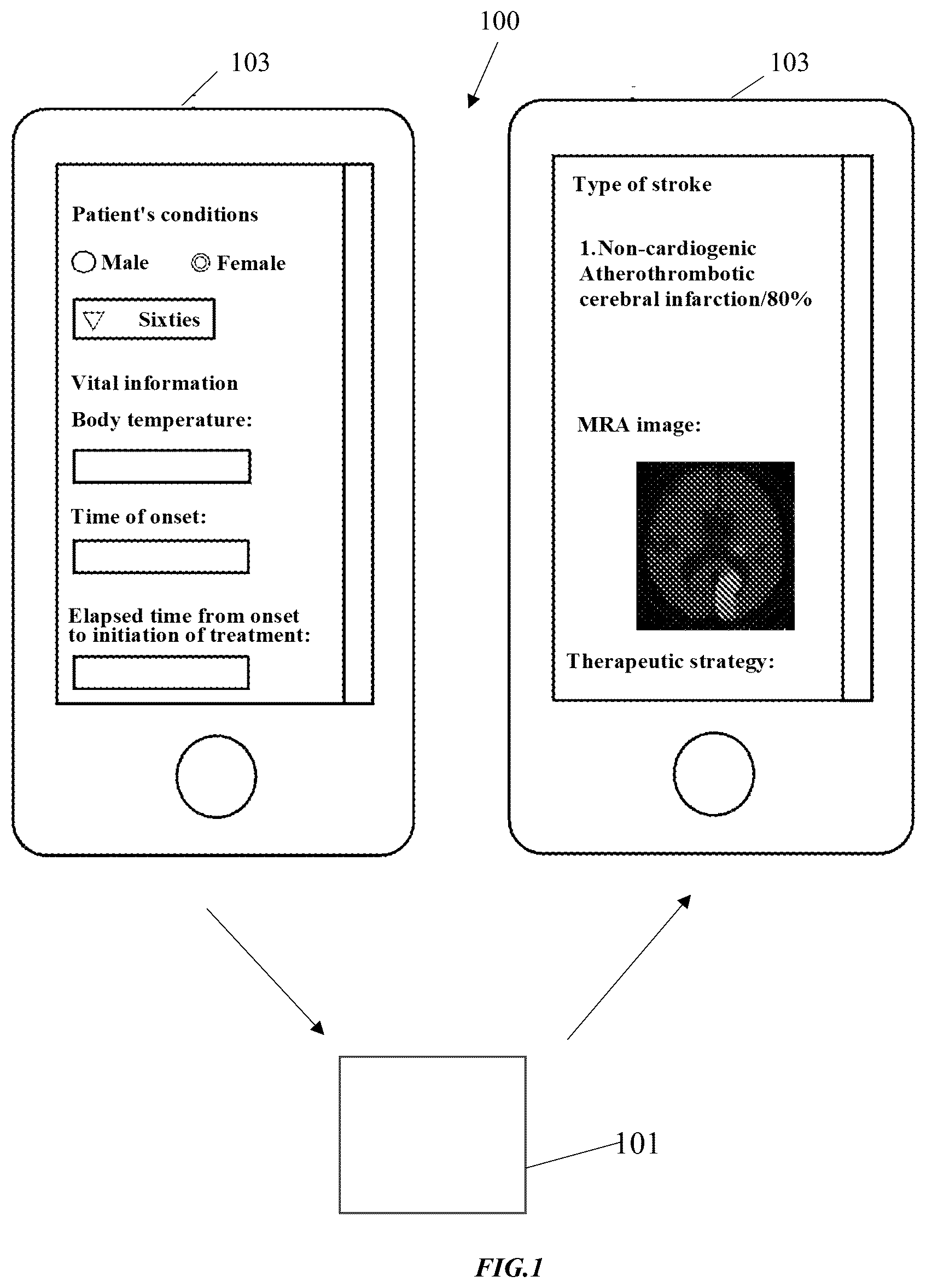
The means for solving the problems in the present invention and effects of the invention are shown below. The system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to present invention has a device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke and a device for providing information about state of stroke, and uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed, to provide information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that assists diagnosis/treatment of stroke. The device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke has a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images as the information of images, a unit of laboratory finding acquirer that acquires the information about laboratory findings, a unit of stroke type determiner that has been trained to use predetermined information of images and predetermined information about laboratory findings to determine information about type of stroke corresponding thereto, and uses the acquired information of images and information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke, a unit of therapeutic strategy acquirer that acquires a corresponding therapeutic strategy from information about therapeutic strategy wherein the therapeutic strategy previously associated with the type of stroke is described, based on the determined type of stroke, and a unit of information provider for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that provides the determined type of stroke and acquired therapeutic strategy as information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke. The device for providing information about state of stroke has a unit of image provider that provides the information of images, a unit of information acquirer for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that acquires the information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and a display unit that displays the acquired information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke. As a result, information necessary for treatment can be easily provided to those who do not have sufficient knowledge about treatment of stroke by using predetermined information of images and information about laboratory findings. The device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to present invention uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed to assist diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and has a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images as the information of images, a unit of laboratory finding acquirer that acquires the information about laboratory findings, a unit of stroke type determiner that has been trained to use predetermined information of images and predetermined information about laboratory findings to determine information about type of stroke corresponding thereto, and uses the acquired information of images and information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke, a unit of therapeutic strategy acquirer that acquires a corresponding therapeutic strategy from information about therapeutic strategy wherein the therapeutic strategy previously associated with the type of stroke is described, based on the determined type of stroke, and a unit of information provider for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that provides the determined type of stroke and acquired therapeutic strategy as information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke. As a result, the type of stroke that can be estimated from each information of images can be obtained by simply providing information of images and information about laboratory findings. That is, even those who do not have expert knowledge about stroke can be assisted so as to be able to diagnose appropriately the type of stroke and perform its treatment. In the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to present invention, the unit of stroke type determiner is characterized by further using the information about infarction regions wherein the size, number, and position of the infarction region, responsible vessels for the infarction region, and their number are determined and the information about occlusions/stenoses wherein the presence or absence of intracranial stenoses is determined, for a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring, by using the information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images, to determine the type of cerebral infarction, and furthermore, having been trained to determine from the predetermined information about infarction regions and the predetermined information about occlusions/stenoses, the type of cerebral infarction corresponding thereto. As a result, the type of stroke can be determined more accurately, since a unit of stroke type determiner trained by using existing information about infarction regions and occlusions/stenoses is used. In the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to present invention, the unit of stroke type determiner is characterized by having a unit of cerebral infarction region determiner that uses the information of DWI and ADCmap to determine a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring by, and that the unit of cerebral infarction determiner has been trained to determine from the predetermined information of DWI and ADCmap, the cerebral infarction region corresponding thereto. As a result, cerebral infarction regions can be determined more easily and accurately, since a unit of cerebral infarction region determiner trained by using existing information of DWI and ADCmap is used. In the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to present invention, the unit of stroke type determiner is characterized by having a unit of responsible vessel determiner that determines responsible vessels from the information about three-dimensional position of the predetermined cerebral infarction regions, and that the unit of responsible vessel determiner has been trained to be able to determine from the information about three-dimensional position of the predetermined cerebral infarction regions, the responsible vessels corresponding thereto. As a result, the responsible vessels corresponding to the information about three-dimensional position of cerebral infarction regions can be determined more easily and accurately, since a unit of responsible vessel determiner trained by using the existing information about three-dimensional position of cerebral infarction regions is used. The program for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to present invention makes a computer function in the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed, to assist diagnosis/treatment of stroke, as a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images as the information of images, a unit of laboratory finding acquirer that acquires the information about laboratory findings, a unit of stroke type determiner that has been trained to use predetermined information of images and predetermined information about laboratory findings to determine information about type of stroke corresponding thereto, and uses the acquired information of images and information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke, a unit of therapeutic strategy acquirer that acquires a corresponding therapeutic strategy from information about therapeutic strategy wherein the therapeutic strategy previously associated with the type of stroke is described, based on the determined type of stroke, and a unit of information provider for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that provides the determined type of stroke and acquired therapeutic strategy as information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke. As a result, the state of stroke that can be estimated from each information of images can be obtained by simply providing predetermined information of images and information about laboratory findings to a computer. That is, even those who do not have expert knowledge about stroke can be assisted so as to be able to determine the state of stroke easily. The model for determination of the type of cerebral infarction of the present invention is characterized by making a computer function as a unit of stroke type determiner that uses the information about infarction regions wherein the size, number, and position of the infarction region, responsible vessels for the infarction region, and their number are determined and the information about occlusions/stenoses wherein the presence or absence of intracranial stenoses is determined, for a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring, by using the information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images, to determine the type of cerebral infarction, and that furthermore, the unit of stroke type determiner has been trained to determine from the predetermined information about infarction regions and the predetermined information about occlusions/stenoses, the type of cerebral infarction corresponding thereto. As a result, a model for determination of the type of stroke trained by using existing information about infarction regions and occlusions/stenoses can be constructed in a computer, and the type of stroke can be determined more accurately by using the constructed model for determination of the type of stroke. The model for determination of cerebral infarction regions according to present invention is characterized by making a computer function as a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI and ADCmap of the brain and a unit of cerebral infarction region determiner that determines a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring by using the information of DWI and ADCmap, and that the unit of cerebral infarction determiner has been trained to determine from the predetermined information of DWI and ADCmap, a cerebral infarction region corresponding thereto. As a result, a model for determination of cerebral infarction regions trained by using existing information of DWI and ADCmap can be constructed in a computer, and cerebral infarction regions can be determined more easily and accurately by using the constructed model for determination of cerebral infarction regions. The model for determination of responsible vessels according to present invention is characterized by making a computer function as a unit of responsible vessel determiner that determines responsible vessels from the information about three-dimensional position of a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring, and that the unit of responsible vessel determiner has been trained to be able to determine from the information about three-dimensional position of the predetermined cerebral infarction regions, the responsible vessels corresponding thereto. As a result, a model for determination of responsible vessels trained by using existing information about three-dimensional position of a cerebral infarction region can be constructed in a computer, and the responsible vessels corresponding to the information about three-dimensional position of a cerebral infarction region can be determined more easily and accurately by using the constructed model for determination of responsible vessels. The example of the present invention will be described in detail as follows with reference to drawings. The device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to the present invention is described by using the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 100 shown in I. Configuration of Hardware 1. The System for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke 100 The system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 100 comprises a device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 and a device for providing information about state of stroke 103. The device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 and the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 are connected by a predetermined network, and can send and receive information to each other via the predetermined network. When the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 acquires from the device for providing information about state of stroke 103, the information of CT images (described later), DWI (described below), MRA images (described below) that indicate the state of stroke, information about conditions of a subject being diagnosed who is a patient, and information about laboratory findings based on various tests, it estimates the type of stroke based on accumulated information about diagnosis/treatment of stroke wherein the data of diagnosis/treatment of stroke obtained so far are accumulated from the acquired information of CT images, DWI, MRA images, information about conditions of the subject being diagnosed, and information about laboratory findings, and estimates corresponding therapeutic strategy. The device for providing information about state of stroke 103 provides the information of CT images, DWI, ADCmap, MRA images, information about conditions of a subject being diagnosed, and information about laboratory findings that relate to the state of strike of the subject being diagnosed who is likely to be in a state of stroke, to the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 via a network. In addition, the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 acquires from the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101, the type of stroke and the therapeutic strategy estimated from the sent information of CT images, DWI, ADCmap, MRA images, information about conditions of the subject being diagnosed, and information about laboratory findings and displays them. As a result, users of the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 can easily obtain necessary information for treatment of stroke, even if they do not have sufficient knowledge about its treatment. 2. The Device for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke 101 The configuration of hardware of the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 is described with reference to The CPU 101 The keyboard 101 3. The Device for Providing Information about State of Stroke 103 The configuration of hardware of the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 is described with reference to The CPU 103 The display 103 II. Information Used Information used in the watch over system 100 is described with reference to 1. Information about State of Stroke The information about state of stroke indicates the state of stroke of a subject being diagnosed, that is, a patient. The data structure of the information about state of stroke is shown in In the region describing conditions of a subject being diagnosed, the information about conditions of a subject being diagnosed that indicates conditions of the subject being diagnosed is described. The gender, age, body temperature of the subject being diagnosed, time of onset, elapsed time from the onset to initiation of treatment, and the like are described in the region describing conditions of a subject being diagnosed. In the region describing CT images, information of CT images of a subject being diagnosed is described. In the region describing DWI images, information of DWI of a subject being diagnosed is described. In the region describing ADCmap, information of ADCmap of a subject being diagnosed is described. In the region describing MRA images, information of MRA images of a subject being diagnosed is described. In the region describing laboratory findings, information about laboratory findings related to predetermined items determined from examinations, etc. performed on a subject being diagnosed is described. The information described in each description region is described below. (1) Information about Conditions of a Subject being Diagnosed The information about conditions of a subject being diagnosed relates to examinations determined from those performed on a subject being diagnosed whose conditions are to be determined, by using the system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 100. The data structure of the information about conditions of a subject being diagnosed is shown in (2) Information of CT Images The information of CT images indicates brain images of a subject being diagnosed acquired by using CT (computer tomography). The information of CT images is generated with a CT device operated by a physician or the like. An example of information of CT images is shown in (3) Information of DWI The information of DWI indicates a type of sequence of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging wherein the diffusion motion of water molecules is imaged. The DWI (diffusion weighted image) is generated with a DWI device operated by a physician or the like. An example of information of DWI is shown in (4) Information of ADCmap The information of ADCmap shows imaged apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) obtained from a plurality of DWI obtained by adding a dephasing effect by changing the strength and application time of the gradient magnetic field in the pulse sequence of the spin echo method. The information of ADCmap is generated with an ADCmap device operated by a physician or the like. An example of information of ADCmap is shown in (5) Information of MRA Images The information of MRA images shows vessel images of a subject being diagnosed acquired by using MRA (magnetic resonance angiography). The information of MRA images is generated with an MRA device operated by a physician or the like. An example of information of MRA images is shown in (6) Information about Laboratory Findings The information about laboratory findings relates to state of a disease determined from examinations performed on a subject being diagnosed, that is, a patient, whose conditions are to be determined, by using the system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 100. The data structure of the information about laboratory findings is shown in 2. Information about Therapeutic Strategies The information about therapeutic strategies is a database wherein state of stroke and therapeutic strategies to be used for treatment are associated. The data structure of the information about therapeutic strategies is shown in 3. Information for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke The information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke indicates the type of stroke of a subject being diagnosed estimated from the information about state of stroke acquired from the subject being diagnosed and therapeutic strategy corresponding thereto. By providing the information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke, a physician who is less inexperienced in the diagnosis and treatment of stroke is assisted so as to be able to perform appropriate diagnosis and treatment. The data structure of the information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke is shown in In the region describing estimated type of stroke, information about determined type of stroke indicating the estimated type of stroke of a subject being diagnosed based on the information described in the regions describing conditions a subject being diagnosed, CT images, DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images of the information about state of stroke (see In the information about therapeutic strategies, a therapeutic strategy extracted from the information about therapeutic strategies (see (1) Information for Determining Type of Stroke The data structure of the information for determining type of stroke is shown in The “non-cardiogenic lacunar infarction” refers to the infarction not caused by a heart disease, but caused by thrombi generated in artery and clogging of fine arteries in the brain. In addition, the “non-cardiogenic atherothrombotic cerebral infarction (ATI)” refers to the infarction caused by the curing of carotid artery from the neck to the brain and relatively thick arteries in the brain (atherosclerosis). Furthermore, the “cardiogenic cerebral embolism (CE)” refers to the infarction caused by that the thrombi generated in the heart flow into the arteries in the brain to cause the vessels in the brain to be clogged. II. Operation of the System for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke 100 The operation of the system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 100 is described with reference to 1. Operation (1) of the Device for Providing Information about State of Stroke 103 The operation of the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 is described with reference to the flowchart shown in A user of the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 (referred to as a user hereinafter) activates the program for providing information about state of stroke of the device for providing information about state of stroke 103. When the CPU 103 When the CPU 103 An overview of the operation of the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 is described with reference to the flowchart shown in The CPU 101 The CPU 101 The CPU 101 The processing for generation of information about intracranial hemorrhage, the processing for generation of information about infarction regions, the processing for generation of information about occlusions/stenoses, the processing for determination of types of cerebral infarction, and the processing for generation of information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke are described below. 1. The Processing for Generation of Information about Intracranial Hemorrhage The processing for generation of information about intracranial hemorrhage is described with reference to the flowchart shown in When the CPU 101 2. The Processing for Generation of Information about Infarction Regions The processing for generation of information about infarction regions is described with reference to the flowchart shown in Variation in DWI occurs due to differences in DWI devices such as manufacturers and models, individual differences such as thickness of vessel of subjects being imaged, conditions of subjects being imaged at the time of imaging, and the like. For this reason, in the pre-processing of images, image correction regarding brightness, rotation, and position, etc. on the acquired DWIs is performed to reduce the variation between the DWIs. The CPU101 The processing for extraction of infarction regions is described with reference to As the amount of characteristic for the pixels of candidate infarction, information about three-dimensional position and left-right symmetry of the pixels of candidate infarction, pixel values of ADCmap pixels corresponding to pixels of candidate infarction of DWI (referred to as corresponding ADCmap candidate pixels hereinafter), and surrounding pixel values of the corresponding ADCmap candidate pixels are used. DWI is an image of the degree of molecules' Brownian motion and is characterized in that the pixel value turns higher in an infarction region where diffusion is limited. On the other hand, since the DWI is a kind of T2-weighted image, the region with a high pixel value in a T2-weighted image may result in a higher pixel value even if the corresponding region of the DWI does not have any diffusion limit, which is referred to as T2 shine-through. Upon interpreting, in order to distinguish between the region where the infarction is actually occurring and the region of the T2 shine-through, a physician not only considers the DWIs but also ADCmap images at the same time. In the region where the infarction is occurring, the pixel value in DWI turns higher than the surroundings, while the pixel value in ADCmap turns lower than the surroundings. On the other hand, in the region of T2 shine-through, even if the pixel value in DWI is higher than the surroundings, the pixel value in ADCmap dose not turn lower than the surroundings. Therefore, the pixel values of not only DWI but also ADCmap are used as the amount of characteristic in order to distinguish the infarction region from the region of T2 shine-through. The CPU 101 It is noted that in the processing for determination of infarction regions, a model for determination of infarction regions trained to calculate infarction regions has been constructed in advance from DWI, ADCmap, and the amount of characteristic of several cases reviewed by physicians. Returning to In addition, the CPU 101 The processing for determination of responsible vessels is a processing for determining, from the calculated information about three-dimensional position of the determined infarction regions, the position of determined infarction regions whether a determined infarction region is present in the cortical branch or in a narrow branch, and for determining responsible vessels. The responsible vessels are classified into six types, including basilar artery (BA), anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA), posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA), middle cerebral artery (MCA), anterior cerebral artery (ACA), and posterior cerebral artery (PCA). The vessels except basilar artery (BA) exist symmetrically on left and right sides, however, the left ones and right ones are not distinguished in the processing for determination of responsible vessels. Besides, decision trees are used as algorithm in the processing for determination of responsible vessels. It is noted that in the processing for determination of responsible vessels, a model for determination of responsible vessels trained to calculate whether a determined infarction region is present in the cortical branch or in a narrow branch from the information about three-dimensional position of infarction regions, and responsible vessels for infarction regions has been constructed in advance. The CPU 101 The CPU 101 The CPU 101 An example of the generated information about infarction regions is shown in 3. The Processing for Generation of Information about Occlusions/Stenoses (1) Summary When a vascular occlusion occurs, a vessel beyond a region where a vascular occlusion is occurring disappears from an image captured using magnetic resonance angiography (referred to as MRA images hereafter). Therefore, it is difficult to directly determine from MRA images the region where a vascular occlusion is occurring, which is a problem. On the other hand, when a vascular stenosis occurs, the vessel where the stenosis is occurring exists in MRA images. For this reason, the region where a vascular stenosis is occurring can be determined directly from MRA images. Therefore, due to the characteristic difference between vascular occlusions and stenoses in MRA images, the occurrence of vascular occlusions and stenoses is determined respectively by processing for determination of occlusions and processing for determination of stenoses. An overview of the processing for determination of occlusions/stenoses is shown in the flowchart of Thereafter, the CPU 101 (2) The Processing for Determination of Occlusions As described above, it is difficult to determine directly from MRA images a region where a vascular occlusion has occurred. Thus, a vascular occlusion is detected by utilizing structure of configuration of vessels in the brain, specifically the left-right symmetrical structure, and focusing on the fact that a large difference in blood flow between the left and right side of the brain occurs when a vascular occlusion is occurring. The processing for determination of occlusions is described with reference to the flowchart shown in For the detection of occlusions in internal carotid artery (ICA) in the lower half of the region and for the detection of occlusions in the artery after middle cerebral artery (MCA) in the upper half of the region, the brain is divided into upper and lower parts. Besides, because the basilar artery at the center of lower half of the brain may tortuous somehow, a portion of the center is excluded from the regions to be calculated for the volume. The CPU 101 When the value of index is “0.5 or higher” (S1807), the CPU 101 (3) The Processing for Determination of Stenoses The processing for determination of stenoses is described with reference to the flowchart shown in The CPU 101 The CPU 101 The CPU 101 In the processing for determination of the name of a vessel, the name of a vessel is determined from the three-dimensional data and the width of the vessel extracted. It is noted that in the processing for determination of the name of a vessel, a model for determination of the name of a vessel trained to calculate the name of a vessel has been constructed in advance by using the three-dimensional data and the width of several vessels. The CPU 101 When the CPU 101 4. The Processing for Determination of the Type of Cerebral Infarction In the processing for determination of the type of cerebral infarction, Bayesian network is used as algorithm. The Bayesian network has the following characteristics. Results of determination can be acquired as values of probability. Even in cases of lack in some of input items, results of determination can be inferred from other items. The relationship between amounts of characteristic can be visualized. When considering operations in clinical practice, the second characteristics described above is particularly important. In actual clinical practice, not all test data are available at the time when a determination is desired, and some items are more likely missing. Thus, the Bayesian network, where inference can be performed even in cases of defects, has significant advantages compared to other approaches. The CPU 101 In the processing for determination of the type of cerebral infarction, a plurality of possible names of the type of cerebral infarction paired with their likelihood (%) are generally calculated as the information about the type of cerebral infarction. It is noted that in the processing for determination of the type of cerebral infarction, a model for determination of the type of cerebral infarction trained to be able to determine the type of cerebral infarction has been constructed in advance by using the information about infarction regions, occlusions/stenoses, and laboratory findings of several cases previously reviewed by physicians. In the process of the constriction of the model for determination of the type of cerebral infarction, contribution rates corresponding to the type of cerebral infarction used in Bayesian network are calculated for the information about infarction regions, occlusions/stenoses, and laboratory findings. 5. The Processing for Generation of Information for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke The processing for generation of information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke is described with reference to the flowchart shown in The CPU 101 3. Operation (2) of the Device for Providing Information about State of Stroke 103 Returning to When a user of the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 has made a conclusion that the treatment based on the displayed information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke is possible, the necessary treatment is performed. (1) Sending/Receiving Various Information of Images and Information for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke In Example 1 described above, various information of images and information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke are sent/received via wireless network between the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 and the device for providing information about state of stroke 103. However, they may also be sent/received by using wired lines. (2) Recipients of Information for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke In Example 1 described above, the information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke is sent to the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 to which each information of images has been sent. However, it may also be sent to other designated communication devices. In addition, it may also be sent to other designated communication devices and the device for providing information about state of stroke 103 to which information of images has been sent. (3) The Configuration of Hardware of the Device for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke 101 In Example 1 described above, the CPU 101 (4) The Configuration of Hardware of the Device for Providing Information about State of Stroke 103 In Example 1 described above, a smartphone is used in the device for providing information about state of stroke 103. However, other devices, such as a dedicated device, may also be used. Furthermore, although the CPU 103 (5) The Program for Assisting Diagnosis/Treatment of Stroke and the Program for Providing Information about State of Stroke In Example 1 described above, the program for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke achieves the processing according to the illustrated flowchart. However, it is not limited to the example as long as it achieves the similar processing. The same can be said for the program for providing information about state of stroke. Furthermore, the algorithms used in each model is not limited to the example as long as it can exhibit similar functions. (6) Neurological Findings Furthermore, in Example 1 described above, neurological findings for presuming classic lacunar syndrome, such as the presence or absence of the clinical evidence such as any of pure motor hemiparesis, pure sensory seizures, ataxic hemiplegia, dysarthria, unilateral dexterity, cerebral cortical infarction (aphasia, agnosia, apraxia, unilateral spatial agnosia, etc.), or cerebellar infarction (dizziness, nausea) may also be used as the information about neurological findings to estimate the type of stroke. The system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to the present invention can be used, for example, for a medical support system used in a medical institution that does not have any person with professional knowledge about stroke. [Problems] Provision of a system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke which can easily provide supportive information so that the type of stroke can be determined appropriately and corresponding treatment strategy can be implemented. [Solutions] When the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101 acquires information of CT images, DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images indicating state of stroke from the device for providing information about state of stroke 103, it uses the acquired information of images and the information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke in a unit of stroke type determiner trained to use the predetermined information of images and the predetermined information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke corresponding thereto. The device for providing information about state of stroke 103 provides each information of images indicating state of stroke of a subject being diagnosed, to the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101, acquires and displays the type of stroke and therapeutic strategy determined from the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke 101. 1. A system for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke which has a device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke and a device for providing information about state of stroke, uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed, to provide information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that assists diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and is characterized in that
the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke has
a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images as the information of images, a unit of laboratory finding acquirer that acquires the information about laboratory findings, a unit of stroke type determiner that has been trained to use predetermined information of images and predetermined information about laboratory findings to determine information about type of stroke corresponding thereto, and uses the acquired information of images and information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke, a unit of therapeutic strategy acquirer that acquires a corresponding therapeutic strategy from information about therapeutic strategy wherein the therapeutic strategy previously associated with the type of stroke is described, based on the determined type of stroke, and a unit of information provider for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that provides the determined type of stroke and acquired therapeutic strategy as information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and the device for providing information about state of stroke has
a unit of image provider that provides the information of images, a unit of information acquirer for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that acquires the information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and a display unit that displays the acquired information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke. 2. A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke which uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed to assist diagnosis/treatment of stroke, and has
a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images as the information of images, a unit of laboratory finding acquirer that acquires the information about laboratory findings, a unit of stroke type determiner that has been trained to use predetermined information of images and predetermined information about laboratory findings to determine information about type of stroke corresponding thereto, and uses the acquired information of images and information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke, a unit of therapeutic strategy acquirer that acquires a corresponding therapeutic strategy from information about therapeutic strategy wherein the therapeutic strategy previously associated with the type of stroke is described, based on the determined type of stroke, and a unit of information provider for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that provides the determined type of stroke and acquired therapeutic strategy as information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke. 3. A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke characterized in that
furthermore, the unit of stroke type determiner in the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to furthermore, the unit of stroke type determiner has been trained to determine from the predetermined information about infarction regions and the predetermined information about occlusions/stenoses, the type of cerebral infarction corresponding thereto. 4. A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke characterized in that
furthermore, the unit of stroke type determiner in the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to the unit of cerebral infarction determiner has been trained to determine from the predetermined information of DWI and ADCmap, the cerebral infarction region corresponding thereto. 5. A device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke characterized in that
furthermore, the unit of stroke type determiner in the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke according to the unit of responsible vessel determiner has been trained to be able to determine from the information about three-dimensional position of the predetermined cerebral infarction regions, the responsible vessels corresponding thereto. 6. A program for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that makes a computer function in the device for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that uses predetermined information of images that relates to stroke of a subject being diagnosed and information about laboratory findings that indicates the laboratory findings of the subject being diagnosed, to assist diagnosis/treatment of stroke, as a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images as the information of images,
a unit of laboratory finding acquirer that acquires the information about laboratory findings, a unit of stroke type determiner that has been trained to use predetermined information of images and predetermined information about laboratory findings to determine information about type of stroke corresponding thereto, and uses the acquired information of images and information about laboratory findings to determine the type of stroke, a unit of therapeutic strategy acquirer that acquires a corresponding therapeutic strategy from information about therapeutic strategy wherein the therapeutic strategy previously associated with the type of stroke is described, based on the determined type of stroke, and a unit of information provider for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke that provides the determined type of stroke and acquired therapeutic strategy as information for assisting diagnosis/treatment of stroke. 7. A model for determination of the type of cerebral infarction, characterized by making a computer function as a unit of stroke type determiner that uses the information about infarction regions wherein the size, number, and position of the infarction region, responsible vessels for the infarction region, and their number are determined and the information about occlusions/stenoses wherein the presence or absence of intracranial stenoses is determined, for a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring, by using the information of DWI, ADCmap, and MRA images, to determine the type of cerebral infarction, and that
furthermore, the unit of stroke type determiner has been trained to determine from the predetermined information about infarction regions and the predetermined information about occlusions/stenoses, the type of cerebral infarction corresponding thereto. 8. A model for determination of cerebral infarction regions, characterized by making a computer function as a unit of image acquirer that acquires information of DWI and ADCmap of the brain and a unit of cerebral infarction region determiner that determines a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring by using the information of DWI and ADCmap, and that
the unit of cerebral infarction determiner has been trained to determine from the predetermined information of DWI and ADCmap, a cerebral infarction region corresponding thereto. 9. A model for determination of responsible vessels, characterized by making a computer function as a unit of responsible vessel determiner that determines responsible vessels from the information about three-dimensional position of a cerebral infarction region where a cerebral infarction is occurring, and that
the unit of responsible vessel determiner has been trained to be able to determine from the predetermined information about three-dimensional position of the cerebral infarction regions, the responsible vessels corresponding thereto.TECHNICAL FIELD
BACKGROUND
PRIOR ART LITERATURE
Patent Literature
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Problems to be Solved by the Invention
Effects of the Invention
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Example 1
OTHER EMBODIMENTS
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
DESCRIPTION OF NOTATIONS